
Meteorological disasters feature a wide range of influence, high frequency of occurrence, and large losses. They account for more than 70% of China's natural disaster losses.
With “integration” as the guiding idea for construction, cloud-based architecture and big data technology as the carrier, and One Map as the support for display, SuperMap has completed the construction of a comprehensive risk survey platform for meteorological disaster with functions such as data management, information collection, risk assessment, and risk zoning.
1. Let the data “speak”: Find out the bottom line of meteorological disaster risk
The comprehensive risk survey of meteorological disasters involves 9 types of disasters, each type of disaster includes foundation data, disaster-forming environment data, hazard-bearing body data, hazard-causing factor data, disaster data, questionnaire data, etc. There are many categories, and each type of disaster data is different, and each type of data cannot be obtained at one time, such as the meteorological disaster survey form. This increases the difficulty of the work of operating personnel and related managers.
Based on the source of all data resources, operation usage methods, update time, and administrative attribution, the platform combines GIS spatial locations to vividly present different types of data in front of users through graphic combination and chart linkage.
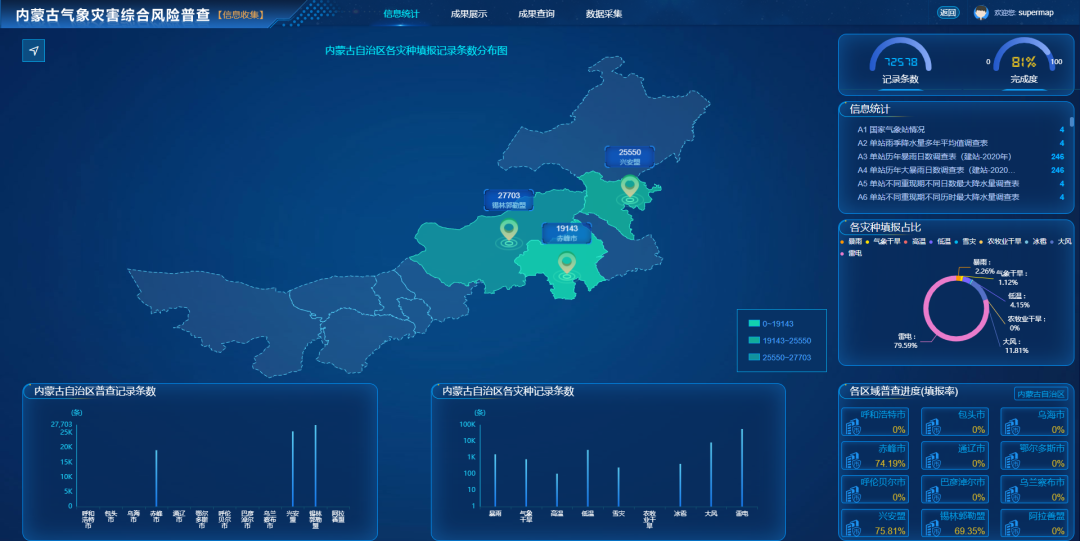
2. “Portrait” of data: Grasp the law of meteorological disasters
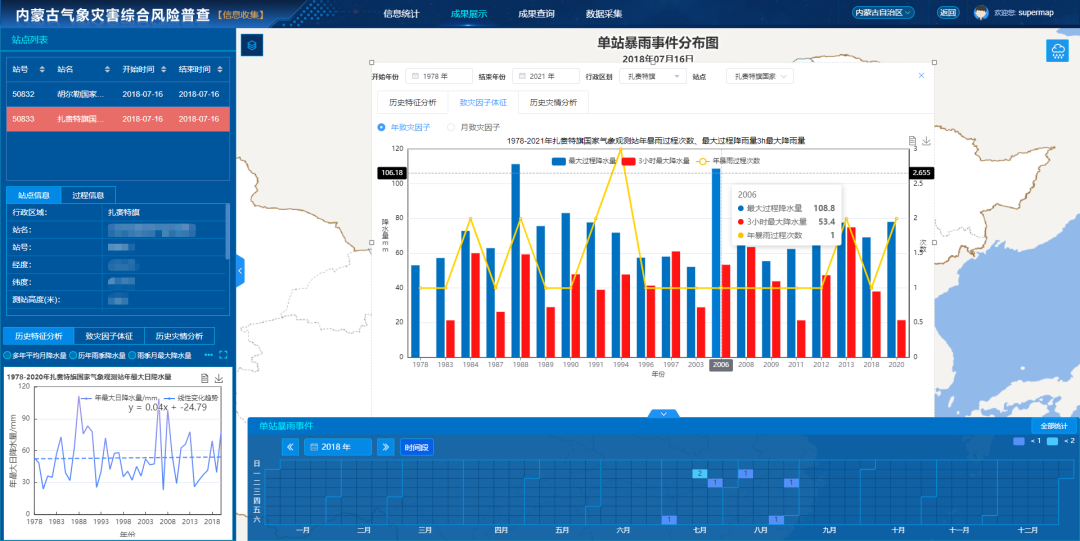
The occurrence of meteorological disasters is closely related to disaster-causing factors, disaster-forming environments, and disaster-bearing bodies. However, whether it is the disaster situation collected through sorting out or the disaster events identified through model algorithms, they are independent data and its overall situation and historical laws cannot be effectively displayed.
According to different types of disasters and data characteristics, the platform combines WebGIS technology, chart visualization technology, time axis, etc., to display and analyze the spatial distribution characteristics, historical evolution rules and correlations between related factors from time and space, and provide users with a platform for observing, summarizing, and analyzing the laws of meteorological disasters.
3. Let the function “walk”: Build a general survey process of meteorological disaster risk
Starting from the natural disaster risk census process, the platform considers the connection and progressive relationship between the subsystem division and function design, especially in the functional design of the two subsystems of meteorological disaster risk and risk zoning, which fully reflects the relations of functions. Users only need to follow the sequence of function design and operate step by step to complete the corresponding data calculation and production. In terms of details, each step provides a variety of ways for users to choose, such as scientific calculation and customization, and builds a standardized and flexible operation process.
4. Let the platform “grow”: Build a meteorological disaster risk management operation system
Natural disaster risk census is a phased task. Based on meeting the phased goals, the platform has a scalable design for data update, model calculation, result display and analysis, etc. Users can use the technology and results formed during the risk census process for day-to-day operations. By accessing real-time data, the platform can conduct meteorological disaster risk monitoring and risk assessment; by accessing forecast data, the platform can perform meteorological disaster risk prediction and risk estimation.
From data to algorithms, from models to products, from monitoring and evaluation to forecasting, the platform has built a complete meteorological disaster risk management business system, providing effective support for the disaster prevention and mitigation business of meteorological disasters.
The risk census platform can strengthen data applications, and display disaster-causing factors, disaster-affected body information, and census results in various ways. Based on the big data cloud platform, some functions of the climate operation integration platform have been preliminarily realized, providing data, technology and platform support for the general survey and risk management of meteorological disasters in Inner Mongolia. The Inner Mongolia meteorological disaster risk zoning and assessment service platform, through designing a data center, adding a disaster risk survey one map, add a framework N base N application architecture, achieves the integrated functions of query display, assessment and zoning operation application, and supports the future risk management operation development.
--Director of Climate Center of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region