The frequency of natural disasters brings obstacles to the rapid development of cities. A key point in building a “smart city” is how to “smart” deal with natural disasters’ impacts on cities. Natural disaster prevention and mitigation is an important part of the smart city emergency response system. The monitoring, early warning, assessment, response and recovery of natural disasters can be carried out by means of information technology, which will greatly improve the comprehensive emergency management level of cities and help the construction and development of smart cities.
Natural Disaster Prevention and Mitigation System
The disaster prevention and mitigation of natural disasters can be interpreted from multiple dimensions such as disaster dimension, industry dimension, business dimension, and time dimension:
1. Disaster dimension: According to the causes and characteristics of disasters, it is generally divided into meteorological disasters, flood and drought disasters, geological disasters, forest and grass fires, marine disasters, earthquake disasters, etc.
2. Industry dimension: Disaster + industry, such as agricultural meteorological disasters, power meteorological disasters, etc.
3. Operation dimension: The whole business process of disaster management, including disaster risk zoning, disaster investigation, disaster monitoring, disaster early warning, risk assessment, impact assessment, disaster response, disaster recovery, etc.
4. Time dimension: The disaster management is divided according to the time scale. The large scale of time includes the past (historical disaster investigation, risk zoning), the present (current disaster monitoring, early warning, risk assessment, etc.), and the future (disaster prediction, impact, etc.) Pre-assessment); the small scale of time is to divide the operation into the pre-disaster (monitoring, early warning), during the disaster (impact assessment, disaster response), and after the disaster (recovery and construction).
The comprehensive emergency management platform for urban disaster prevention, mitigation, and relief based on “One Map” covers the entire process of natural disaster emergency management, so as to achieve the normalized management of pre-disaster monitoring and early warning, disaster prevention and control, and disaster release and emergency response during disasters. The combination of abnormal management can conduct early warning before disasters, eliminate hidden dangers, predict and evaluate during disasters, respond effectively, and minimize losses.
“One Map” Solution for Natural Disaster Prevention, Mitigation and Relief in Cities
Natural disasters are typically spatially distributed. Therefore, the monitoring, early warning, evaluation of natural disasters, disaster emergency command and rescue, research and decision-making are inseparable from the support of spatial information and GIS technology. With SuperMap GIS spatial information technology as the core, the “One Map” solution will play an important role in the prevention, mitigation and relief of natural disasters in cities.
“One Map” is to integrate multi-element, multi-temporal and multi-regional basic geographic data and various natural disaster thematic spatial data under a unified geospatial framework. It integrates various dynamically changing information through the association of spatial elements, forming a unified natural disaster emergency management spatio-temporal information database. It constructed spatial information services and spatial information software support to provide stable and reliable natural disaster spatiotemporal services for various industries and departments. It can support the co-construction and sharing of resources of the emergency geographic information layer of natural disaster information in each department. It mainly functions in:
Data support (big data)
“One Map” gathers basic GIS basemap data including vector, terrain, image, BIM, oblique photogrammetry data, etc.; emergency response operation data including protection targets, emergency supplies, rescue forces, shelters, etc., and various disaster perception monitoring data including meteorological disaster monitoring, flood disaster monitoring, fire monitoring, debris flow monitoring, video monitoring, etc.
Application support (workbench)
“One Map” can provide unified, stable, reliable and safe geographic information services and spatial information software development technical support for all disaster emergency management cooperative departments. It includes basic GIS services, disaster emergency management general operation services, quick processing and publication of disaster emergency spatial-temporal data as well as emergency operation secondary development components, etc.
Integrated platform (integrated warehouse)
“One Map”, as an integrated display platform for disaster prevention and mitigation applications, can show natural disaster risk zoning, network monitoring and early warning of major risks, distribution of emergency rescue resources, disaster situation analysis and comprehensive research and judgment, and emergency rescue command and dispatch, emergency rescue tracking, disaster impact assessment, etc. based on the map.
The construction framework of the comprehensive emergency management platform for urban disaster prevention, mitigation, and relief based on “One Map”
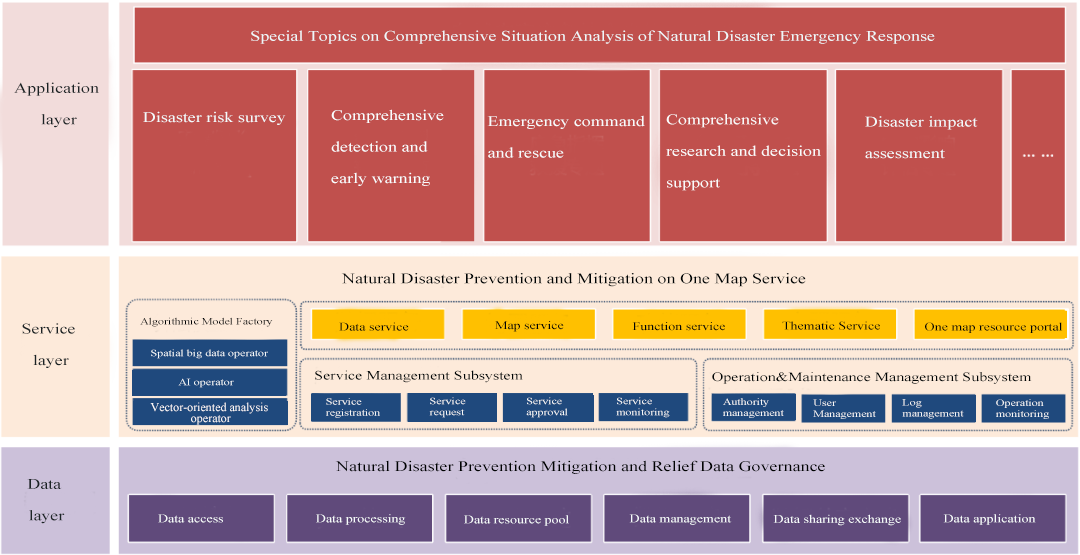
The construction of the platform in the data layer, service layer, and application layer mainly includes:
1. Data governance system: Combined with the disaster prevention and mitigation emergency management needs, it can access and integrate basic data from local government departments in natural resources, ecological environment, transportation, health care, meteorology, etc. It built up the natural disaster emergency data government system and carries out whole-chain governance including data access, processing, storage, application and control. The unified big data resources center based on data aggregation and governance offers services of data sharing, exchanging and application.
2. “One Map” service system: Use the data provided by the data governance system to build algorithm model management, business model development, algorithm development and other capabilities through machine learning, knowledge map and other technologies, and form an algorithm model pool to provide emergency services.
3. Thematic application in disaster risk investigation: Based on the data resource pool and the services provided by the “One Map” service system, build a map of disaster risk investigation, and present historical disaster distribution maps and disaster risk analysis based on the map. It not only includes the disaster risk of each single disaster type, but also comprehensively analyzes the disaster risk of multiple disasters. The comprehensive “risk map” of natural disasters and the “zoning map” of comprehensive prevention and control of natural disasters will be presented intuitively. It can find out the underlying risks and hidden dangers in the jurisdiction, make up for the shortcomings of decentralized censuses and separate statistics by departments and disaster types in the past.
4. Thematic application in comprehensive monitoring and early warning of natural disasters: Access to the monitoring data of the perception network constructed according to the characteristics of natural disasters in the jurisdiction, mainly including the perception data of forest fire risk monitoring stations, the aggregate displacement of geological disasters, cracks, moisture content, water level and other monitoring data and Early warning data, water conservancy projects, hydrology and other perception data of flood and drought disasters, and meteorological perception data such as aggregated data products, forecast products, early warning products and service products of meteorological disasters. “One Map” can conduct the comprehensive display and analysis of real-time disaster monitoring data, statistical data, disaster identification, risk zoning, disaster forecasting, risk assessment, forecasting and early warning, etc.
5. Thematic application in emergency command and rescue: It supports the map positioning and aggregation display of emergency resource information such as danger sources, protection targets, shelters, rescue teams, medical and health care, and material storage warehouses on “one map”. Centering on the location of emergencies, it analyzes resources based on the type and level of emergencies, as well as the radius of resource distribution. By superimposing shelters, rescue teams, material reserves, communication resources, transportation resources, medical and health care and other information, it forms a resource analysis circle, and achieves the quick query, dispatch and tracking of emergency materials, emergency teams, emergency experts, etc. Based on disaster information, material and resource demand information, combined with emergency thematic data and real-time monitoring data, the most appropriate material and resource allocation plan is achieved through analysis and calculation, providing spatial analysis support for the whole process of emergency event processing and assisting leaders in emergency command.
6. Thematic application in comprehensive research and decision support: Integrate geographic information technology with cloud computing, big data, Internet of Things, mobile Internet and other new-generation information technologies, and achieve comprehensive research and analysis of natural disaster emergency rescue functions based on “One Map”, including:
6.1 Relevant research and judgment of pre-plan cases: According to the disaster information filled in by emergency duty guards, the intelligent matching technology is used to correlate with relevant pre-plans, cases, departments, response levels, proposed opinions, etc., to provide technical support for the preliminary research and judgment of incidents.
6.2 Analysis of disaster trends: After an emergency event occurs, it is necessary to effectively monitor the trends of the event to reduce secondary disaster losses. Through the comprehensive dynamic monitoring of the accident site, the system analyzes the event status in time according to the accident disaster fluctuation curve, and displays it visually with data and charts, allowing decision makers to learn the accident dynamics and trends.
6.3 Analysis of accident impact: When an emergency event occurs, the system automatically evaluates the impact of the event according to the event type and real-time data. At the same time, according to the surrounding geographical elements and socio-economic data of the event, relying on GIS spatial analysis and overlay analysis, it automatically measures the impact of the event on the surrounding area and the scope of social impact.
6.4 Judgment of personnel evacuation plan: Based on the results of accident disaster trend analysis and impact scope analysis, the population evacuation model is used to determine the personnel emergency evacuation plan, and the personnel in the accident area are evacuated in time. It analyzes the severely affected areas that need to be evacuated, finds places that can be placed within a certain range (hospitals, schools, open spaces, etc.), find nearby medical institutions, blocks surrounding roads, deploys evacuation action teams, and determine evacuation routes for evacuation. At the same time, based on factors such as weather conditions and population distribution, the system recommends and delineates the isolation and evacuation range in geographic information, including densely populated areas, schools, commercial areas, key protection areas, protected areas, and water sources.
6.5 Judgment of rescue forces: After an emergency occurs, to ensure the effectiveness of the emergency response, the rapid input of rescue forces is crucial. Aiming at the deployment of rescue forces, the system will coordinate the deployment plan of rescue materials, rescue teams and departments.
7. Thematic application in disaster impact assessment: Based on various types of disaster loss assessment models, predict the scope and affected area of danger at different times, apply the spatial analysis function of GIS, obtain information on people, buildings, and economic activities in the area, and finally estimate disaster losses.
8. Thematic application in emergency comprehensive situation analysis: For the dashboard of the emergency command center, the visual analysis engine is used to construct data visualization analysis and business resource visualization analysis in a self-service manner, so as to satisfy the simple, efficient, flexible and diversified visual display and information of information resources. Display requirements. Integrate the data resources of the information system related to natural disaster emergency management, covering daily monitoring and supervision, emergency command and dispatch, research and analysis and other business fields. This function is used in emergency monitoring and command, analysis and judgment, display and reporting and other scenarios.