The digital twin power plant requires an upgrade and transformation of the geospatial framework of the power plant. It is necessary to build a unified space-time big data sharing platform that supports the unified management, scheduling and sharing of the space-time resources of the power plant.
Digital Twin Power Plant Solution
SuperMap takes the spatiotemporal data of power plants as the research object, and develops the key technologies and solutions for digital twin smart power plants based on SuperMap GIS platform software.
One set of standards
One set of standards focuses on the standardization of digital twin smart power plants, including data management norms, data update norms, and layer usage norms, and clarifies the entire process of data from production to application.
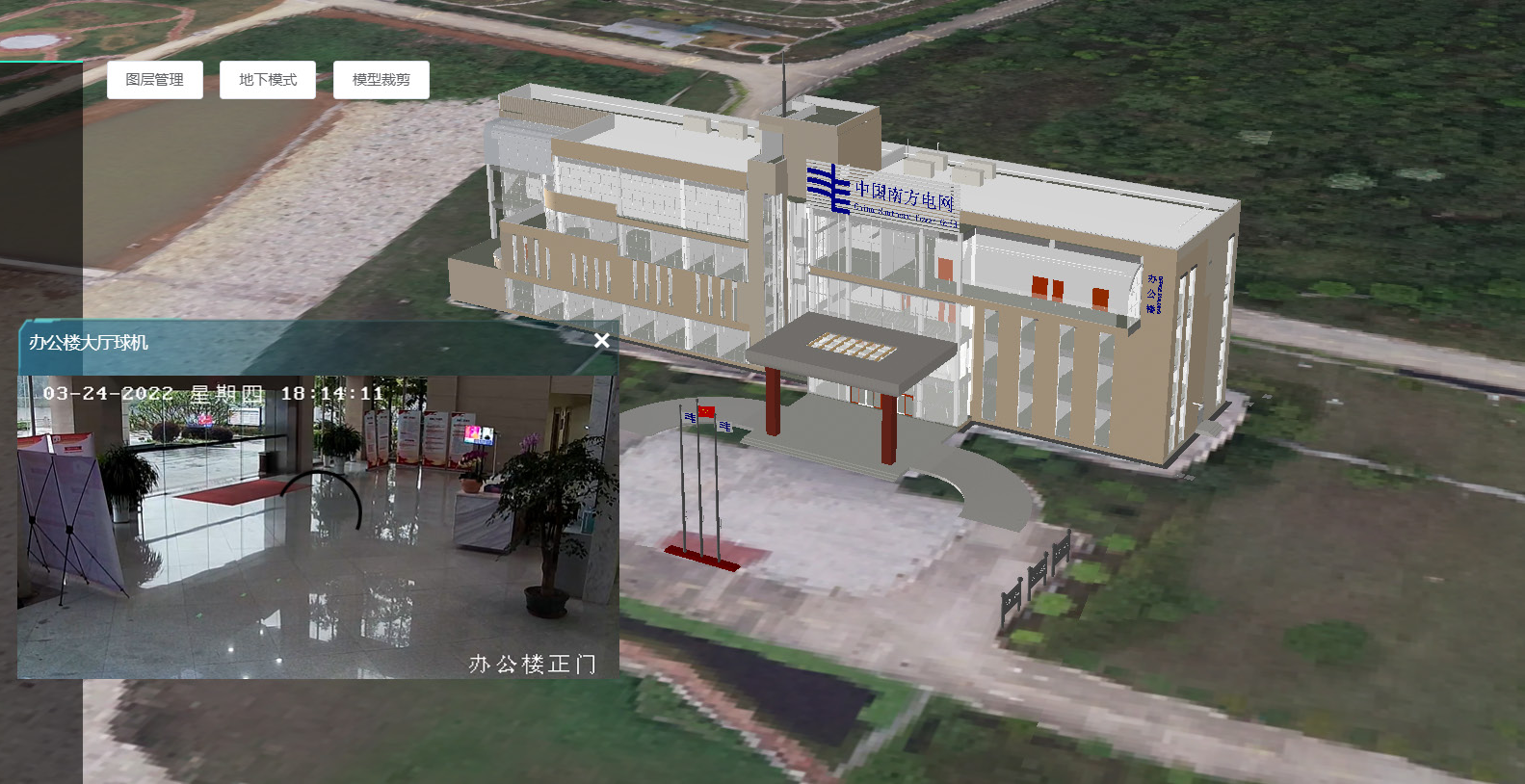

Three databases
The three databases focus on the integration of digital twin smart power plant data, including foundation geographic data, features data, and intelligent perception data, building a spatiotemporal big data warehouse of power plant resources.
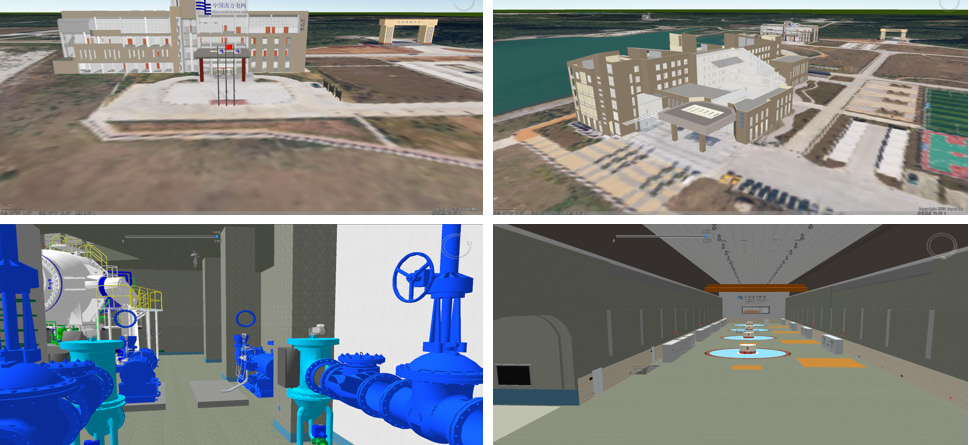
One system
One system focuses on the management, display, and analysis of power plant data, and performs a detailed, comprehensive, and dynamic simulation of the power plant space.
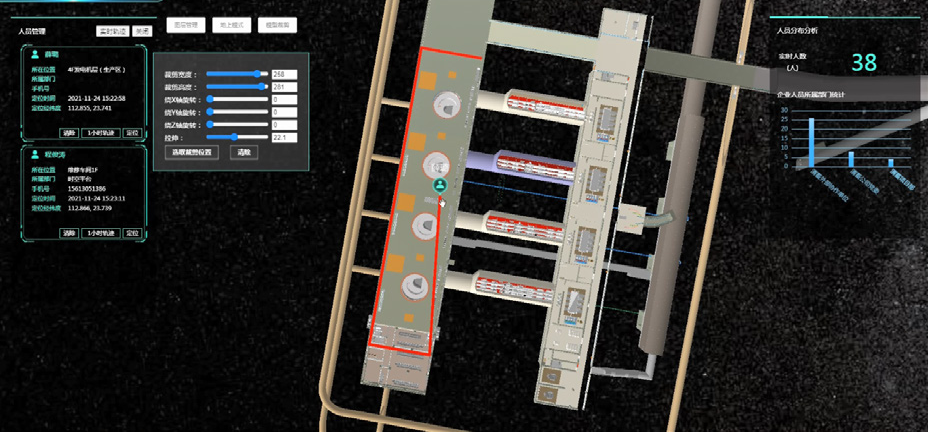
Key Technologies and Innovative Methods
Microservice Architecture
The platform is built based on the microservice architecture, and the overall architecture revolves around five parts: the facility layer, the GIS engine layer, the data layer, the geographic service layer, and the platform application layer.

1. The infrastructure layer is at the bottom of the entire platform, built on platform software and hardware resources, and provides an operating system for the data layer.
2. The GIS engine layer provides the GIS engine components required for building the entire platform, which can integrate spatiotemporal data, build databases and publish data services, and provide a variety of development SDKs to quickly build a cloud-based integrated spatial big data application system.
3. The data layer builds a spatiotemporal database by integrating and accessing the existing spatiotemporal resources of the enterprise, including basic geographic information data, BIM model data, and positioning data, to provide spatiotemporal data support for the service layer and application layer.
4. The geographic service layer is based on the GIS platform and the spatiotemporal database, and provides various spatiotemporal resource services for the application layer, including 2D and 3D map services, data services, and spatial analysis services.
5. The platform application layer builds a map management platform and a comprehensive positioning platform. It conducts the integrated management of enterprises’ space-time resources through the map management platform. The functions include platform power plant service bus, information sharing and exchange center, map service resource management, 2D map drawing, 3D scene, functional service, development center, intelligent operation center and system configuration. The integrated positioning platform can integrate the positioning information of power plants and provide a unified access interface to support data exchange and use with other operating systems.
Data Sharing and Opening Based on iPortal
As the control center of the platform, iPortal enables users to realize WebGIS content management and access control, as well as access methods of various APIs or interfaces, ensuring the implementation of a new web-centric application model. It provides digital twin smart power plants with the following capabilities:
1. GIS resource integration; 2. Fast GIS resource search; 3. Professional online mapping and map browsing; 4. Flexible GIS resource sharing; 5. Visual portal customization; 6. Extended development.
Spatial Big Data Technology
The core technology of spatial big data includes spatial big data storage technology, spatial big data computing technology, stream computing technology and spatial big data visualization technology. At the same time, traditional GIS is reconstructed based on IT big data technology, which supports distributed storage, processing and analysis of massive spatial data, and achieves an order-of-magnitude performance improvement.
In the construction and layout process of smart power plants, data is one of the core assets. Faced with massive spatial data with large volume, wide sources, and fast growth, SuperMap Big Data GIS provides the following for the construction of digital twin smart power plants:
1. The ability to access massive multi-source data based on a unified standard interface;
2. Data engine access capabilities supporting spatial database engines, file storage engines, and distributed storage engines;
3. Big data analysis computing capability, GP service capability, and streaming data service capability;
4. Spatial big data visualization capabilities. The application of Big Data GIS technology helps users simplify workflow, improve processing efficiency, and enhance the presentation experience of digital twin power plants in the actual project construction process.