Precise spatio-temporal data serves as a fundamental geographic information resource for constructing 3D real-world scenes and digital twins. The timeliness of data profoundly impacts its application quality and scope, making data updates critical for maintaining relevance. Traditional full-volume updates require refreshing all data, resulting in long cycles, high costs, and low efficiency.
To address the partial update of 3D oblique photography models, urban fine-grained models, BIM, building white models and other data, SuperMap has launched its multi-source 3D data partial update technology.
This technology accurately identifies changed data and affected areas within the original tile dataset, selectively updating only the necessary portions while reusing unchanged data. This significantly reduces update volume, cuts cost, accelerates frequency, and eliminates the need for service re-publication—effectively maintaining the timeliness of spatio-temporal data and its services.
Partial Updates for Large-Scale Oblique Photography 3D Models
For partial updates of large-scale oblique photography 3D models, SuperMap GIS offers the following capabilities:
Arbitrary-area updates: Breaks the traditional rectangular constraints, enabling precise updates for any shape or scattered points within the source data range.
Historical version management: Automatically records data changes, supporting instant switching between historical versions on desktop, web, and other terminals for easy backtracking and mitigating operational risks.
Precise terminal refresh: Automatically detects changed areas when switching versions, ensuring accurate data refresh and drastically reducing loading time.
Seamless integration of old and new data: Leveraging automatic edge-matching, it intelligently blends updated and existing data for smooth transitions.
Partial Updates for BIM or Urban Fine-Grained Models
For partial updates of BIM or urban fine-grained models, SuperMap GIS provides:
Range-based updates: Incrementally updates geometric objects and their attributes (add/modify/delete) within any specified area, unrestricted by data boundaries, enabling flexible geometry-attribute synchronization.
Object-based updates: Uses unique IDs to quickly locate target objects, supporting dynamic updates of new or modified geometric elements and their attributes at the component level.

Figure 1 Example of Partial Update for BIM Data
Partial Updates for Building White Model Tile Data (Generated via Vector Extrusion)
For partial updates of building white model tile data (generated from extruded vector polygons), SuperMap GIS also supports range-based and object-based updates:
Range-based updates: Dynamically adds, modifies, or deletes building objects and their attributes within any specified area, enabling boundary-free architectural reconstruction.
Object-based updates: Uses unique IDs to pinpoint buildings generated from vector extrusion, allowing real-time object-level updates of structures and their properties.
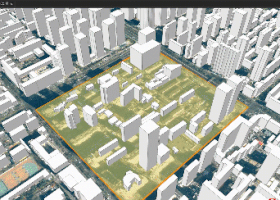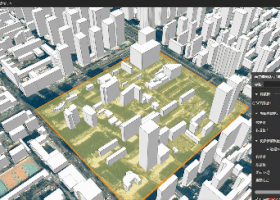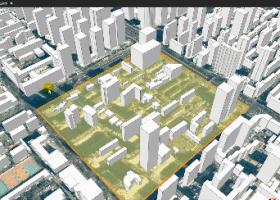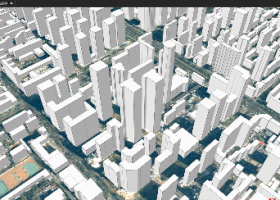
Figure 2 Example of Partial Update for Building White Model Data
Currently, SuperMap's multi-source 3D data partial update technology has been applied in projects such as 3D real-world scene construction and digital twin cities, effectively meeting cross-industry demands for on-demand updates of large-scale multi-source 3D data.
For example, in a test by a surveying institute, a TB-level S3M tile dataset (derived from oblique photography) was updated with around 2GB of new OSGB data. Compared to full-volume updates, SuperMap's technology reduced update time to one-tenth, achieving a 10x efficiency boost.
Moving forward, SuperMap will continue refining this technology to deliver more business-aligned, higher-performance solutions, ensuring seamless implementation for digital transformation initiatives.