SuperMap iServer is a GIS software development platform based on high-performance cross-platform GIS kernal. To better meet user needs, SuperMap continues to improve and upgrade the cloud GIS product over the past year including SuperMap iServer and SuperMap iManager: with high-concurrency dynamic mapping performance optimized, SuperMap iServer newly supports cloud-native data formats such as FlatGeobuf and PMTiles to provide more efficient services; SuperMap iManager newly supports distributed map cutting and other functions to run in a Serverless function, and provides automatic detection of service instance status, automatic alarm and exception repair capabilities.
Optimized high-concurrency dynamic drawing performance
SuperMap iServer has two image rendering methods: dynamic image rendering and cached image rendering. When GIS data is updated frequently, users generally choose to dynamically render maps, that is, instead of generating a cache in advance to satisfy the map request, the server renders the map in real-time every time a map request comes in. However, when concurrent requests are relatively high, it will bring certain challenges to the rendering performance.
SuperMap iServer 2023 has optimized the dynamic rendering logic and improved the performance of high-concurrency dynamic rendering from the following four aspects:
1. The GIS data rendering algorithm has been optimized, and the dynamic raster rendering performance has been improved by about 10 times, as shown in Figure 1:
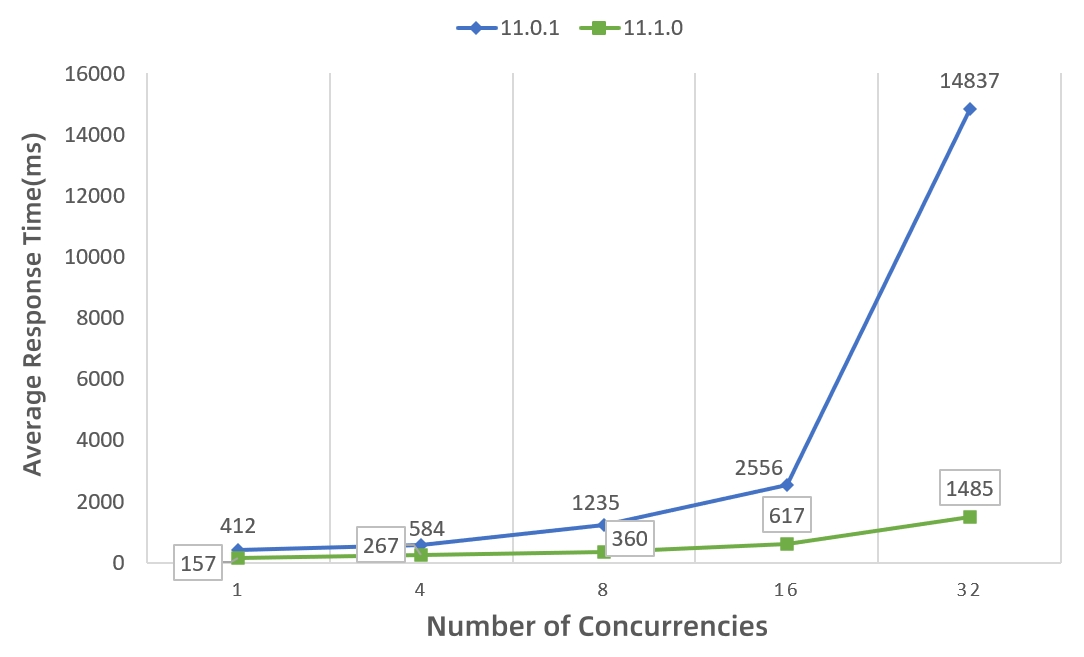
Figure 1 Comparison of average response time of PostGIS engine (10million surfaces + 10million lines) for dynamic raster rendering
2. Based on vector pyramid technology, after creating a vector pyramid, although the volume increases slightly, the dynamic Mapbox Vector Tile (MVT) rendering performance is still improved by more than 15 times, as shown in Figure 2:
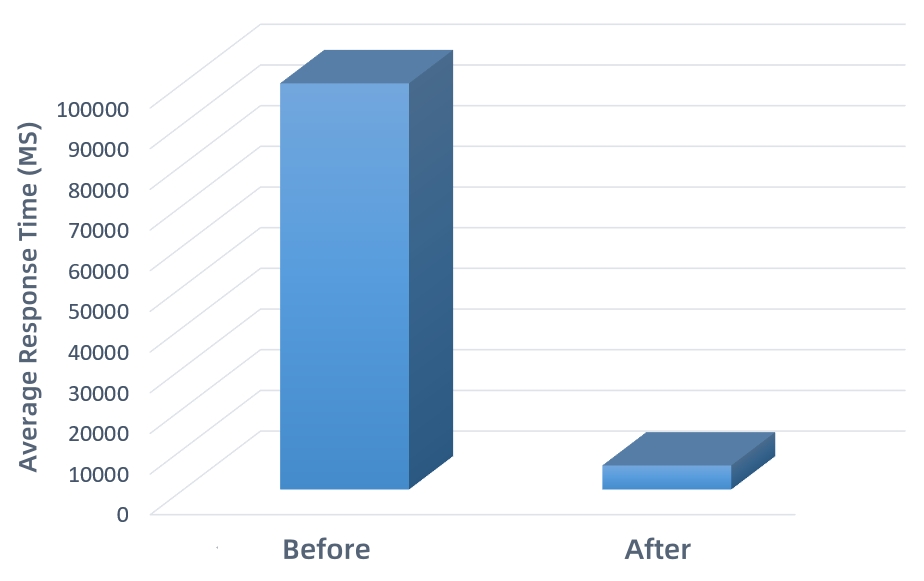
Figure 2 Comparison of average response time of PostGIS engine (10million surfaces + 10million lines) for dynamic MVT rendering
3. Based on image overview technology, after creating an image overview, the dynamic rendering performance of image services at small scales is improved by approximately 100 to 600 times, as shown in Figure 3:
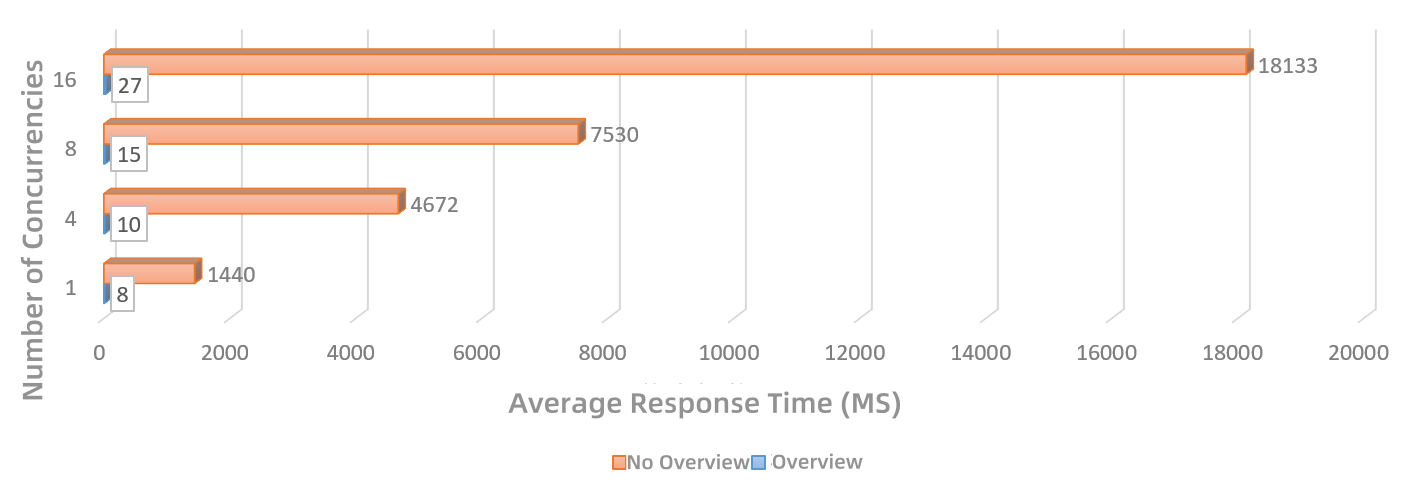
Figure 3 Comparison of small-scale image rendering performance before and after creating an overview
4. The image rendering performance under the dynamic projection of image service has been optimized. The performance is improved by more than 1.5 times under 32 concurrencies (as shown in Figure 4). As the number of concurrencies increases, the performance improvement becomes more obvious.
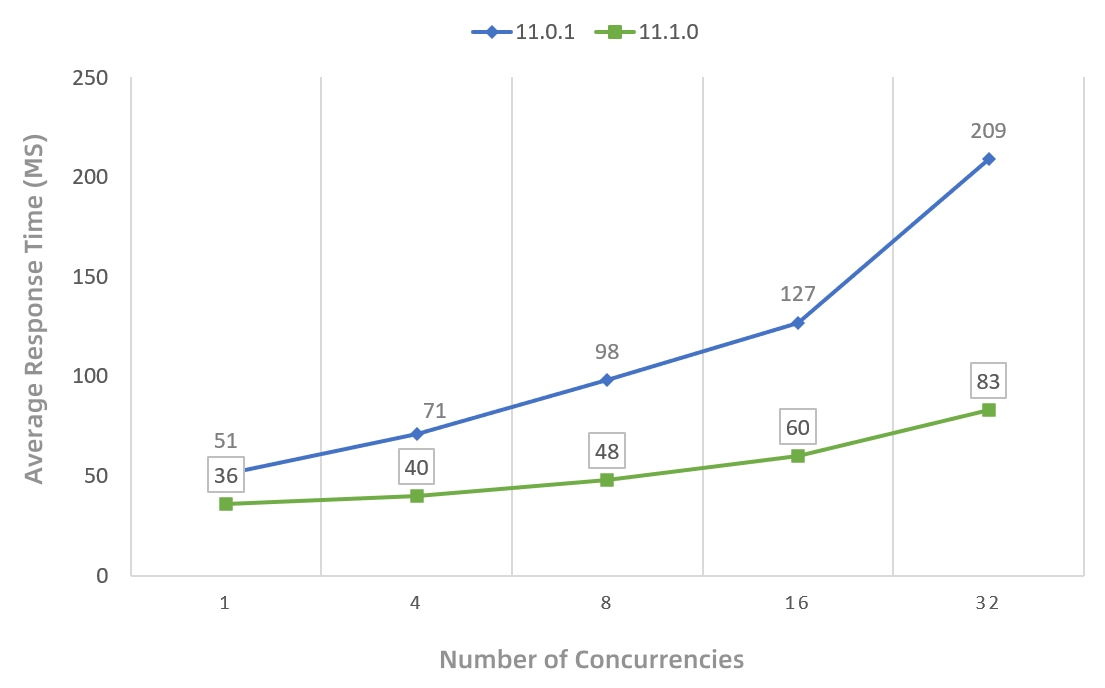
Figure 4 Comparison of average response time of dynamic image rendering under dynamic projection of image service
Query and rendering performance optimization based on FlatGeobuf technology
FlatGeobuf is an open-source data format with a small size. It uses Hilbert R-Tree spatial index, supports fast bounding box spatial filtering (partial loading), and has better client-side rendering performance. Thus, it is recommended as one of the preferred formats by the industry for transmitting spatial data through HTTP/"cloud".
Nearly 20 REST interfaces of SuperMap iServer 2023 such as query and analysis newly support FlatGeobuf (FGB) representation, further improving the transmission and rendering efficiency of query and analysis results.
FGB representation has three major advantages:
1. The upper limit of the amount of data loaded on the web side is larger
Take data query as an example: when the data query results are completely loaded on the Web, the FGB representation can reach 200,000 aspects, which is 10 times the number of GeoJSON, greatly improving the display experience of large-scale data.
2. The representation volume is smaller
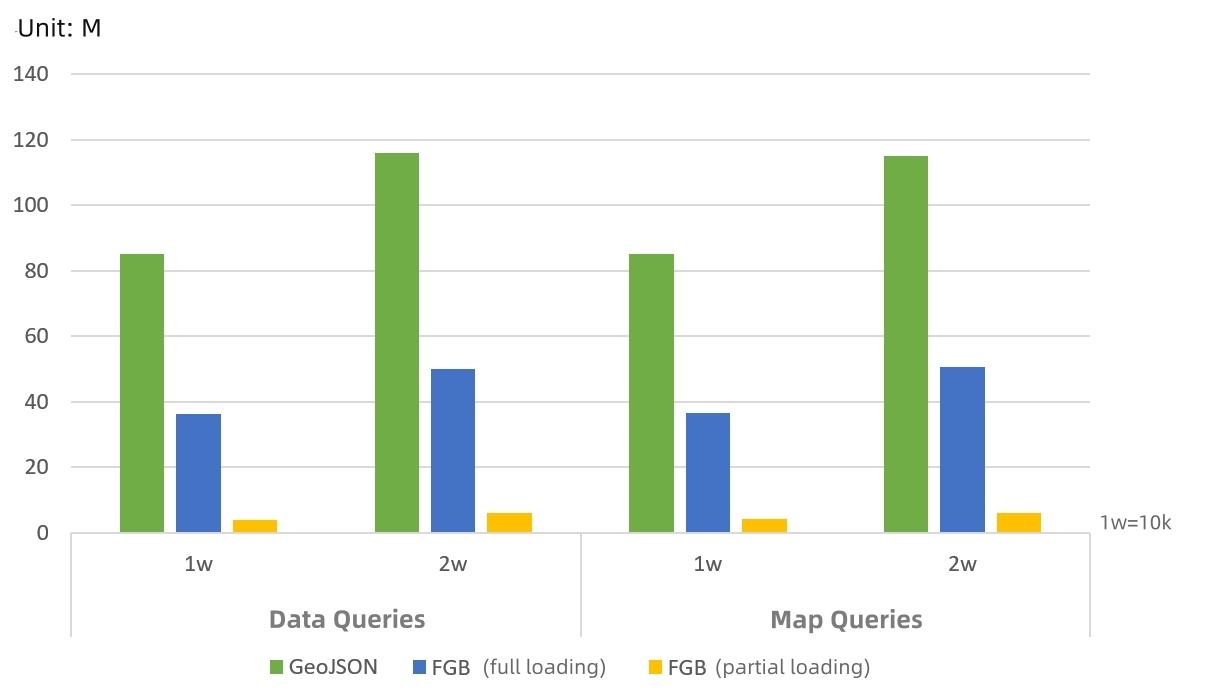
Figure 5 Comparison of query result volume of FGB representation and GeoJSON representation returned by data and map queries
As shown in Figure 5, the query results of FGB returned by data and map queries are about 40% of the GeoJSON representation when fully loaded. The volume of partial loading is smaller than that of full loading, which effectively improves the transmission efficiency of query results.
3. The efficiency of query and rendering is higher
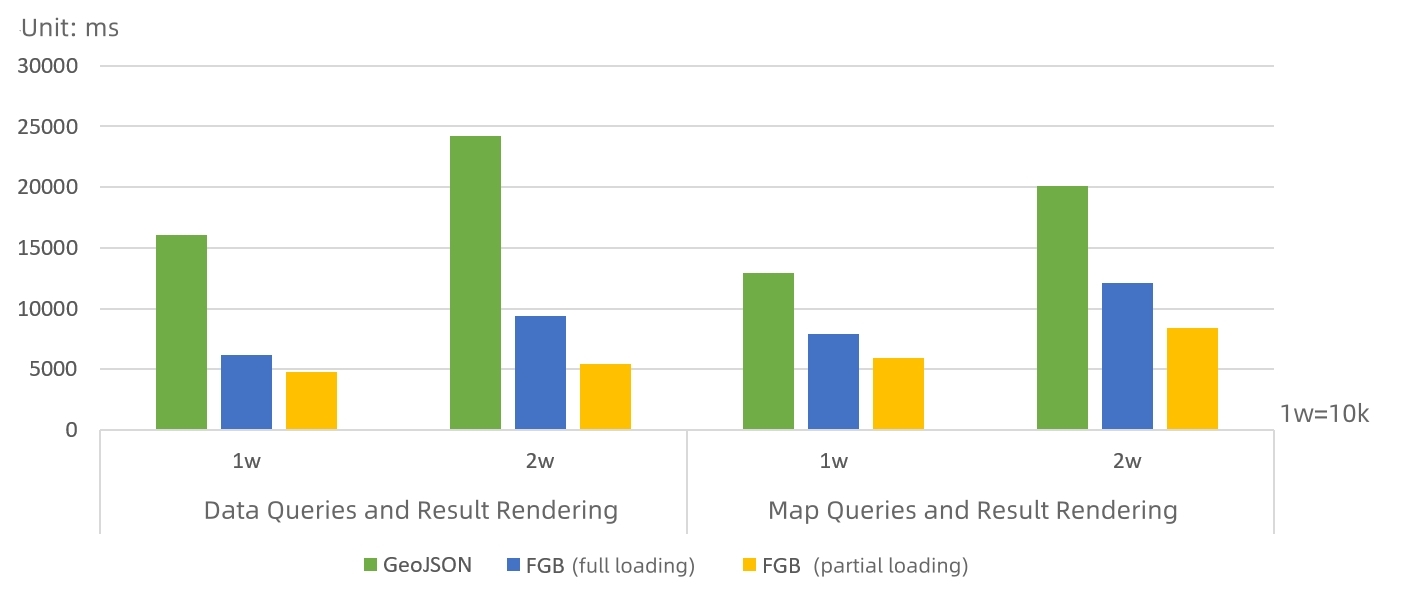
Figure 6 Comparison of the completion time from query execution to web rendering of FGB representation and GeoJSON representation
As shown in figure 6, the efficiency of FGB representation from query execution to web-side rendering is more than three times higher than that of GeoJSON representation, so the partial loading performance is better. The larger the amount of query results returned, the more obvious the advantage.
Serverless functions continue to be updated, making function calculations more flexible yet more stable
Serverless, as a new generation cloud computing model, can greatly improve elasticity and reduce operation and maintenance costs. In 2022, SuperMap applied Serverless to the GIS field, to support spatial analysis services, processing automation (GPA) services, geometry services, mobile alarms and enterprise WeChat remote control functions to run in a functional manner.
In 2023, we newly launched distributed map cutting services and Web printing services that run in serverless function mode. The services run faster, scale more elastically, and thus saving resources to meet in-depth business requirements.
The distributed image cutting service can run in a Serverless function mode, which not only solves the pain point of traditional single-machine image cutting and caching that consume a long time, improves the efficiency, but also has an automatic fault recovery mechanism to ensure stable image cutting on the server side. The capabilities are mainly the following:
1. Under the demand for massive tile production, graph cutting microservices face difficulties such as high computational intensity and long execution time. After being disassembled into functions, automatic elastic scaling and automatic exception recovery are faster, making the GIS system more elastic and resilient.
2. More fine-grained, independent functions are responsible for the cutting, distribution and parallel graph cutting, which improves system stability and high availability.
3. In face of a graph cutting task that consumes huge resources, the function will only be started when there is a task, and the resources will be released immediately after the task execution is completed. In this way, resources will be utilized in a more efficient way.
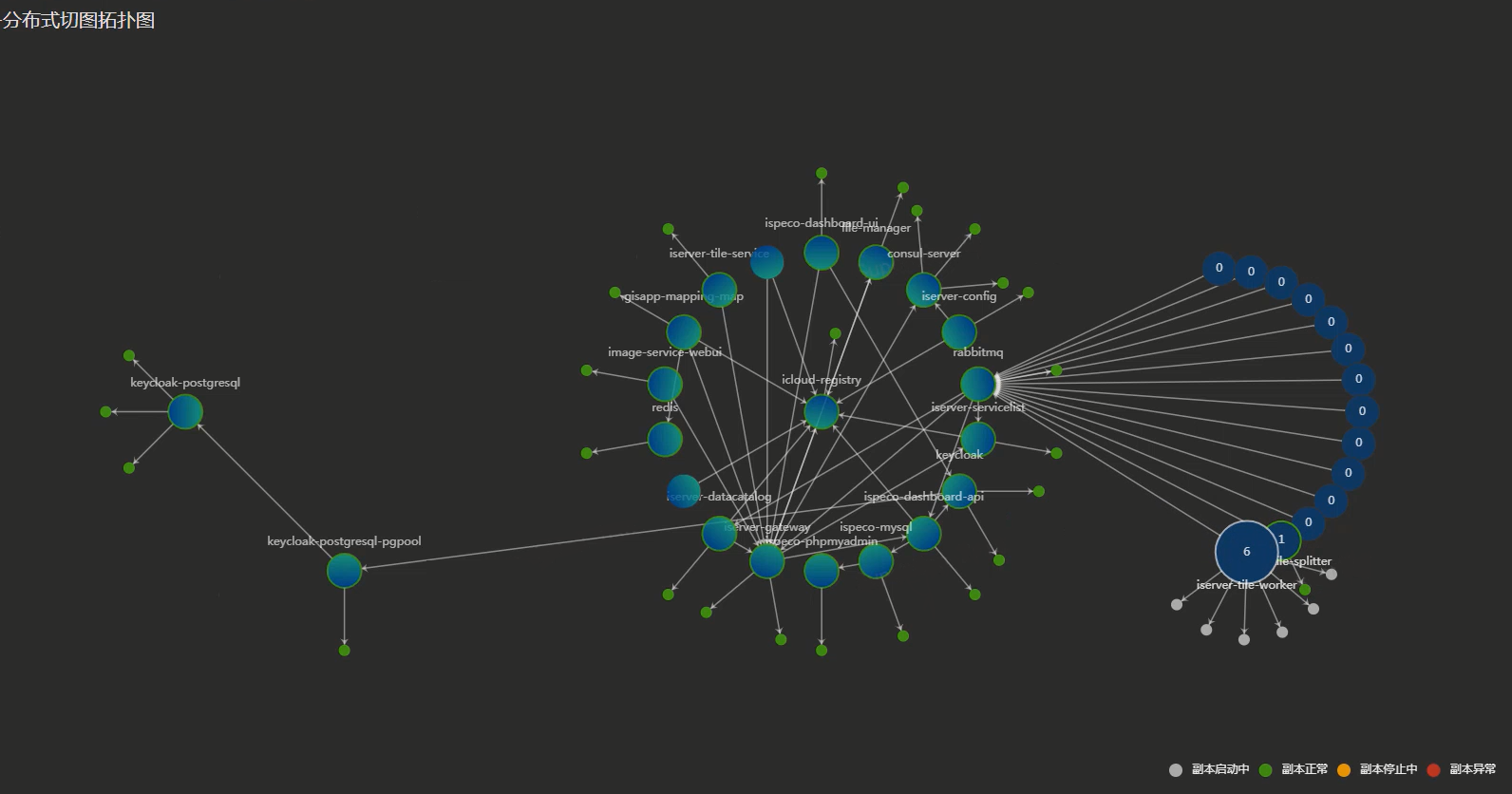
Figure 7 Topology diagram to view functions running on demand
Intelligent detection, alarm and repair of service instance status, making service monitoring more reliable
Faced with a large number of GIS service instances, some abnormal instances can only be checked manually one by one to verify their availability. Not only is the operation and maintenance cost high and inefficient, but it is also difficult to ensure the accuracy of the verification. SuperMap iManager 2023 newly suports service instance status monitoring capabilities mainly including:
1. Support for automatic detection of GIS service instance status, making abnormal services clear at a glance.
2. Providing filtering capabilities based on service status, which can filter out the three statuses of GIS service instances: normal, abnormal, and undetected as needed, and easily locate specific "problem" services with one click.
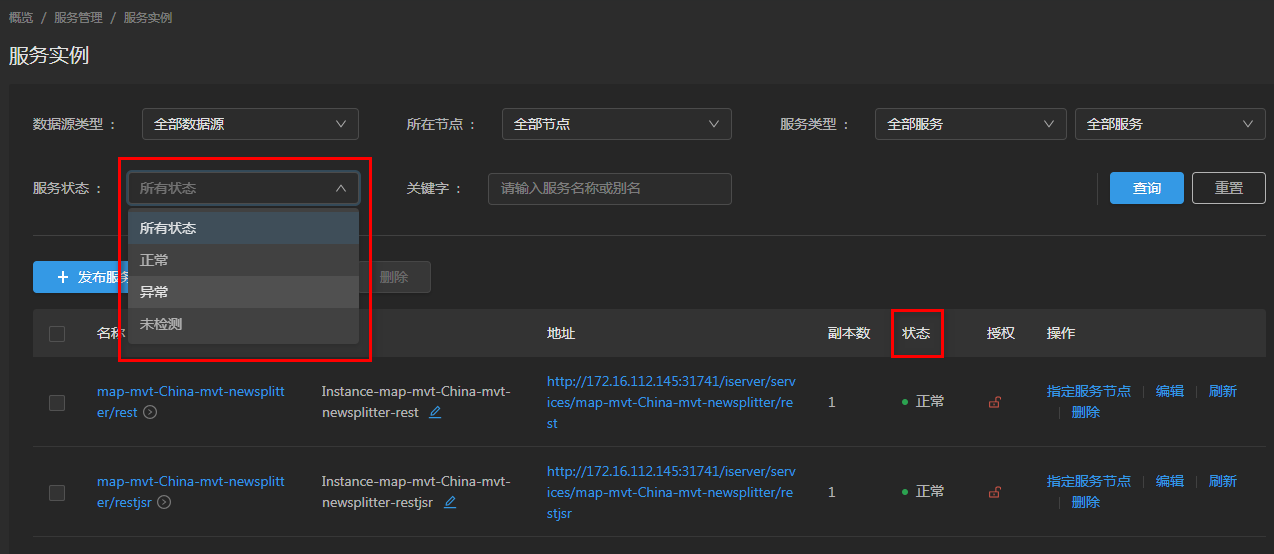
Figure 8 Filtering service instances based on status
3. When the service instance status is abnormal, SuperMap iManager triggers an automatic alarm. It can promptly remind users to understand abnormal service instances.
4. For service instances with abnormal status, the system has added automatic abnormality repair capabilities, which greatly reduces operation and maintenance costs and makes system monitoring more intelligent.
The GIS service instance status monitoring capability improves the practicality and reliability of the product, and provides a "boost" for users to smoothly and efficiently publish services and use GIS systems.