GIS can be implemented as a customized GIS application designed for assist national seacrh and rescues activities. The figure below depicts the architecture of the system.
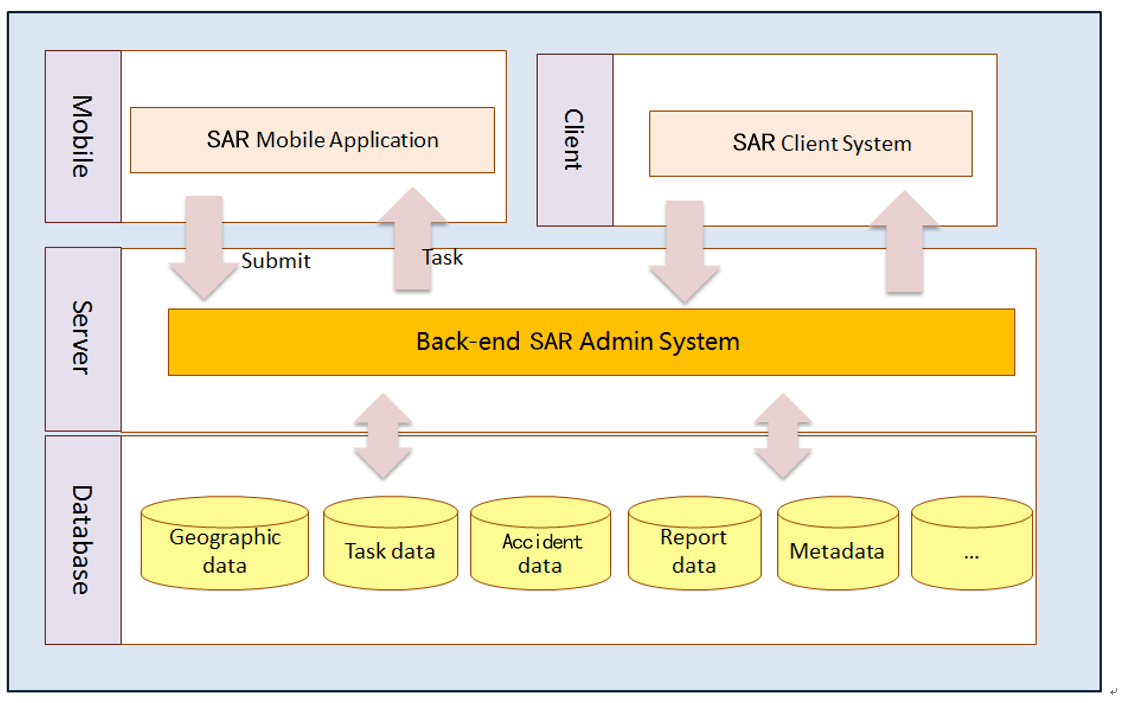
The figure above depicts the architecture of the system. Data is stored in SuperMap SDX+ file database. The database of the system is divided into 5 subsystems: geographic database, task database, accident database, report database, metadata database.
Based on the database, the entire system is composed of a web Client System (Client System), a mobile terminal application (Mobile App), and a back-end administration tool (Admin System).
In order to implement the system, we will prepare but not limited to the following preliminary work:
1. Collect Data for the Initial Startup of System
The SAR system need but not limited to the following data:
National Digital Map, including administrative areas, road, DEM, etcAdministrative Area Data: including administrative area vector polygon data with name and other attributesRoad Network DataDEM
2. Establish Desktop GIS Platform
Prepare and provide current advanced GIS desktop and development software for customers. Establish the exercisable GIS platform for customers. The system, after completed, shall realize the dynamic development, with sustainable update and keep compatibility of the offered software. The system shall also support customers to process enter data into the database if available.
3. Establish GIS Web System for Internal Use of Customer
Prepare and provide a Web GIS System for internal use of customer. The Web GIS System should include, but not limited to, following functions:
Displaying 2D maps and 3D scenes on big screen and touch screen.Manage disaster and accident data on the map of IndonesiaBase maps can be switched among provided choicesSearch disaster or accident information on a map using keywordsFind facilities around a disaster or accident site within specified distancePrint and export maps, query results, and analysis resultsIntegrate with third party web maps like google maps, bing maps, openstreet maps
4. Establish Mobile App
Mobiles Apps are provided for officers and citizens to report accident and clues. The Mobile GIS Apps should include, but not limited to, following functions:
Android and iOS are both supportedViewing accident information in the appQuery accident and disaster resources on the map and do measurementPositioning on the mapReport accident activities to officers.
5. Establish Admin System
Admin system for SAR allows for database management, base map customization, system security control.
Data can be processed and enter into the database if acquired.Basemaps for Web GIS System can be customized and configuredUsers can be managed by groups. Different user groups can be granted different privileges to data and functionsAll the system logs can be viewed and configured.Use cluster to provide GIS services, and establish hot standby protection system with two server.
6. Establish GIS portal system.
The whole system shares some system modules as follows:
A. Client System Module
As the daily operation platform for operators, the Client System consist of 3 modules, including basic GIS module, disaster and accident simulation module, rescue command module.
1. Basic GIS Module
The front-end Client System provides functions such as base map switch, map zoom, map panning, layer control, eagle eye, coordinates display, distance and area measurement, fast query, bookmarks, printing, etc.
Fast query allows customers to select the layer that they want to query and then input key words. The system provides the fuzzy search function. All matched data will be highlighted on the map.
The front-end Client System can display both of 2D map and 3D map on the big Screen.
2. Disaster and Accident Simulation Module
According to the user report accident point. The SAR operator can easily mark the accident position on the map. This module can simulate different effects in the system according to different types of accidents. And show this accident both on the 2D map and in the 3D scene.
Such as the file accident, flood accident, etc.
3. Rescue Command Module
This module can support manager command rescue operations, use the plot symbol to indicate the rescue strategy.
B. Mobile System Module
The mobile application is deployed on the mobile devices of staff working at accident fields. The application provides functions including Basic Map Operations, Mobile Monitoring, New Accident Reporting, Task Management, Accident Data Collection, Accident Data Transfer and Sharing.
1. Map Operations
Map Operations include zooming, panning, full extent, map measurement (distance and area), query, etc. These functions allow the outdoor works to display the surrounding environment in an intuitive way and help measure features.
2. Mobile Monitoring
When GPS and mobile monitoring are enabled, the mobile terminal will report the position data to the database center, allowing managers from officers dynamically track the outdoor workers and manage the tracks.
3. New Accident Reporting
Outdoor workers are able to report new accident while they are working outside. For example, fire location, staffing situation. They will be required to input information for the accident, including attachments in photos. After submission, the new accident will then be added to the map.
4. Task Management
Outdoor workers will be notified with messages when there are new tasks assigned to them from manager. They will then check their task and the place where the task should be carried out on the map. They can view the status of all their tasks and manage the tasks.
C. Back-end Admin System Module
The back-end Admin System is designed to satisfy the needs for database management, front-end map customization, user group management, system security control. Modules of Data Management, Map Management, Log Management, and User Administration are provided.
1. Data Management
Data Management Module primarily focuses on database construction and maintenance. The module provides functions allow SAR operators to process data and enter data into the database.
2. Map Management
This function enables SAR operators to configure base maps. One or multiple base maps can be configured. Each base map corresponds to map in the workspace. Google Maps and Open Street Maps can also be selected as base maps. When there are more than one base map defined, default base map should be defined. Users are allowed to switch to other base maps.
3. Log Management
The system allows SAR officials to monitor the system logs, operation logs and service access logs, and let administrator to do the logs configuration.
4. User Management
The system allows SAR officials to manage the users by groups, different user groups can be granted different privileges to data and functions